UNITED STATES MILITARY RANK ABBREVIATIONS
US AIR FORCE, COAST GUARD, NAVY, MARINES AND ARMY
 |
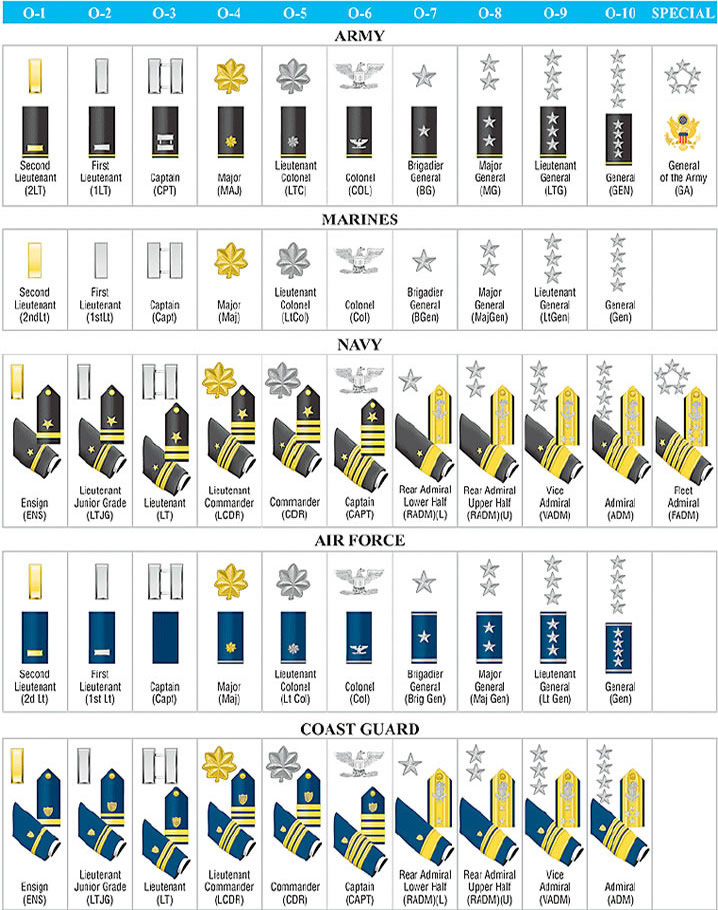
USAF OFFICERS RANK INSIGNIA
US Military Rank Abbreviations
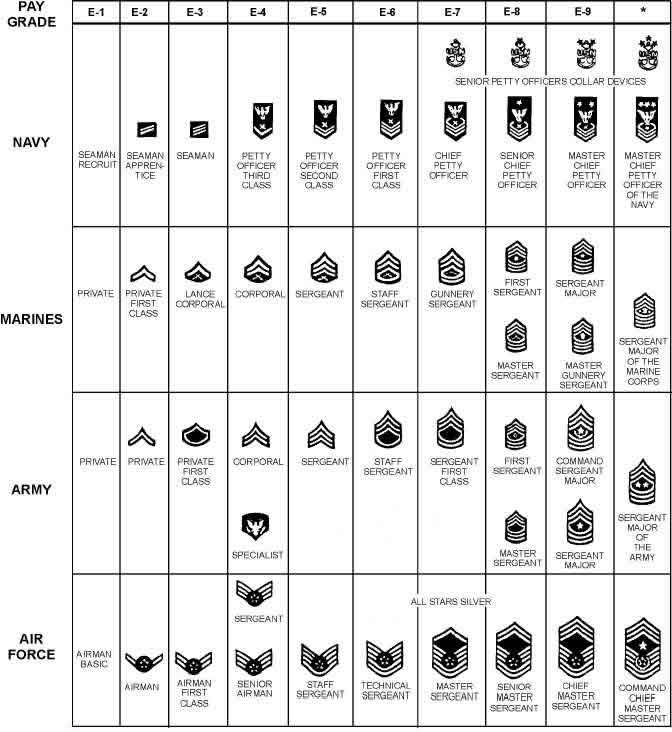
Air Force - NCO's and Officers
| Rate | Rank | Abbrev. | Rate | Rank | Abbrev. |
| E-1 | Airman Basic | AB | O-1 | Second Lieutenant | 2d Lt |
| E-2 | Airman | Amn | O-2 | First Lieutenant | 1st Lt |
| E-3 | Airman First Class | A1C | O-3 | Captain | Capt |
| E-4 | Senior Airman | SrA | O-4 | Major | Maj |
| E-5 | Staff Sergeant | SSgt | O-5 | Lieutenant Colonel | LtCol |
| E-6 | Technical Sergeant | TSgt | O-6 | Colonel | Col |
| E-7 | Master Sergeant | MSgt | O-7 | Brigadier General | BrigGen |
| First Sergeant | 1stSgt | O-8 | Major General | MajGen | |
| E-8 | Senior Master Sergeant | SMSgt | O-9 | Lieutenant General | LtGen |
| First Sergeant | 1stSgt | O-10 | General | Gen | |
| E-9 | Chief Master Sergeant | CMSgt | O-10 | General of the Air Force | |
| First Sergeant | 1stSgt | ||||
| Command Chief Master Sergeant | CCMSgt | ||||
| Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force |
CMSAF |
Army - NCO's and Officers
| Rate | Rank | Abbrev. | Rate | Rank | Abbrev. |
| E-1 | Private | PVT | O-1 | Second Lieutenant | 2LT |
| E-2 | Private | PV2 | O-2 | First Lieutenant | 1LT |
| E-3 | Private First Class | PFC | O-3 | Captain | CPT |
| E-4 | Specialist | SPC | O-4 | Major | MAJ |
| Corporal | CPL | O-5 | Lieutenant Colonel | LTC | |
| E-5 | Sergeant | SGT | O-6 | Colonel | COL |
| E-6 | Staff Sergeant | SSG | O-7 | Brigadier General | BG |
| E-7 | Sergeant First Class | SFC | O-8 | Major General | MG |
| E-8 | Master Sergeant | MSG | O-9 | Lieutenant General | LTG |
| First Sergeant | 1SGT | O-10 | General | GEN | |
| E-9 | Sergeant Major | SGM | General of the Army | ||
| Command Sergeant Major | CSM | ||||
| Sergeant Major of the Army | SMA | ||||
| W-1 | Warrant Officer | WO1 | |||
| W-2 | Chief Warrant Officer 2 | WO2 | |||
| W-3 | Chief Warrant Officer 3 | WO3 | |||
| W-4 | Chief Warrant Officer 4 | WO4 | |||
| W-5 | Master Warrant Officer 5 | WO5 |
Coast Guard - NCO's and Officers
| Rate | Rank | Abbrev. | Rate | Rank | Abbrev. |
| E-1 | Seaman Recruit | SR | O-1 | Ensign | ENS |
| E-2 | Seaman Apprentice | SA | O-2 | Lieutenant Junior Grade | LTJG |
| E-3 | Seaman | SN | O-3 | Lieutenant | LT |
| E-4 | Petty Officer Third Class | PO3 | O-4 | Lieutenant Commander | LCDR |
| E-5 | Petty Officer Second Class | PO2 | O-5 | Commander | CDR |
| E-6 | Petty Officer First Class | PO1 | O-6 | Captain | CAPT |
| E-7 | Chief Petty Officer | CPO | O-7 | Rear Admiral (Lower Half) | RADM (LH) |
| E-8 | Senior Chief Petty Officer | SCPO | O-8 | Rear Admiral (Upper Half) | RADM (UH) |
| E-9 | Master Chief Petty Officer | MCPO | O-9 | Vice Admiral | VADM |
| Command Master Chief Petty Officer | MCPOC | O-10 | Admiral | ADM | |
| Master Chief Petty Officer of the Coast Guard |
MPCO-CG | ||||
| W-2 | Chief Warrant Officer CWO-2 | CWO-2 | |||
| W-3 | Chief Warrant Officer CWO-3 | CWO-3 | |||
| W-4 | Chief Warrant Officer CWO-4 | CWO-4 | |||
Marine Corps - NCO's and Officers
| Rate | Rank | Abbrev. | Rate | Rank | Abbrev. |
| E-1 | Private | Pvt | O-1 | Second Lieutenant | 2ndLt |
| E-2 | Private First Class | PFC | O-2 | First Lieutenant | 1stLt |
| E-3 | Lance Corporal | LCpl | O-3 | Captain | Capt |
| E-4 | Corporal | Cpl | O-4 | Major | Maj |
| E-5 | Sergeant | Sgt | O-5 | Lieutenant Colonel | LtCol |
| E-6 | Staff Sergeant | SSgt | O-6 | Colonel | Col |
| E-7 | Gunnery Sergeant | GySgt | O-7 | Brigadier General | BGen |
| E-8 | Master Sergeant | MSgt | O-8 | Major General | MajGen |
| First Sergeant | 1stSgt | O-9 | Lieutenant General | LtGen | |
| E-9 | Master Gunnery Sergeant | MGySgt | O-10 | General | Gen |
| Sergeant Major | SgtMaj | ||||
| Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps | SgtMajMC | ||||
| W-1 | Warrant Officer | WO-1 | |||
| W-2 | Chief Warrant Officer 2 | CWO-2 | |||
| W-3 | Chief Warrant Officer 3 | CWO-3 | |||
| W-4 | Chief Warrant Officer 4 | CWO-4 | |||
| W-5 | Chief Warrant Officer 5 | CWO-5 |
Navy - NCO's and Officers
| Rate | Rank | Abbrev. | Rate | Rank | Abbrev. |
| E-1 | Seaman Recruit | SR | O-1 | Ensign | ENS |
| E-2 | Seaman Apprentice | SA | O-2 | Lieutenant Junior Grade | LTJG |
| E-3 | Seaman | SN | O-3 | Lieutenant | LT |
| E-4 | Petty Officer Third Class | PO3 | O-4 | Lieutenant Commander | LCDR |
| E-5 | Petty Officer Second Class | PO2 | O-5 | Commander | CDR |
| E-6 | Petty Officer First Class | PO1 | O-6 | Captain | CAPT |
| E-7 | Chief Petty Officer | CPO | O-7 | Rear Admiral (Lower Half) | RDML |
| E-8 | Senior Chief Petty Officer | SCPO | O-8 | Rear Admiral (Upper Half) | RADM |
| E-9 | Master Chief Petty Officer | MCPO | O-9 | Vice Admiral | VADM |
| Master Chief Petty Officer of the Navy | MCPON | O-10 | Admiral | ADM | |
| O-11 | Fleet Admiral | FADM | |||
| W-1 | Warrant Officer First Class | WO1 | |||
| W-2 | Chief Warrant Officer Second Class | CWO2 | |||
| W-3 | Chief Warrant Officer Third Class | CWO3 | |||
| W-4 | Chief Warrant Officer Fourth Class | CWO4 | |||
| W-5 | Chief Warrant Officer | CWO5 |
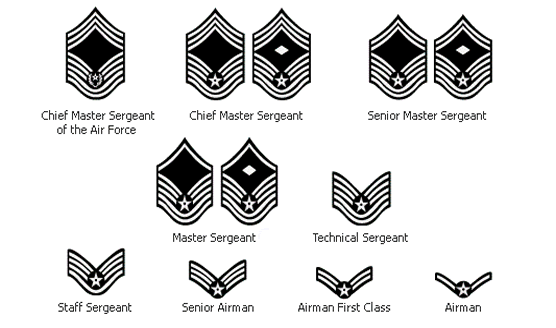
AIR FORCE NON COMMISSIONED OFFICERS (NCO'S)
THE FIRST 5 STAR GENERAL - HENRY H. HAP ARNOLDHap Arnold was a pioneer airman who was taught to fly by the Wright Brothers, and commander of Army Air Forces in victory over Germany and Japan in World War II: born Gladwyne, Pa., June 25, 1886, died Sonoma, Calif., Jan. 15, 1950. "Hap" Arnold, as he was fondly known and called, dating from his early days at West Point, was in the class of 1907 at the U.S. Military Academy. From then on his life paralleled the growth of America's air power and he personally contributed to most of the major milestones of development during the long period until he retired in 1946. Three years later, by act of Congress, he received permanent five-star rank as general of the Air Force, the first such commission ever granted. OFFICER RANK STRUCTURE OF THE UNITED STATES AIR FORCEIn the United States Air Force, General of the Air Force is the highest rank, equivalent to a five star General. The rank has only been held by one person in history: Henry H. Arnold. General of the Army is the equivalent rank in the United States Army and the insignia for the two positions were originally the same. The insignia for General of the Air Force was slightly modified in the 1950s for wear on the new blue Air Force dress uniform. General of the Air Force, however, has never been worn by an officer of the modern Air Force on active duty. Arnold was a General of the Army and retired before the Air Force was made a separate service, but he was awarded the General of the Air Force rank after his retirement and was photographed in an Air Force uniform wearing the insignia of that rank.
During the Cold War, with the rise of the Strategic Air Command, it was proposed that General of the Air Force be reestablished and granted to senior Air Force generals, such as the commander of NORAD. As a result, General of the Air Force can still be seen on modern insignia charts and it is still considered an official rank of the United States Air Force. To date, however, no one except Henry Arnold has ever held the rank General of the Air Force. The United States Navy equivalent of General of the Air Force is Fleet Admiral. A General is an officer of high military rank. The term is used by nearly every country in the world. General may be a rank on its own, or can be used as a generic term for "general officers". In most nations, the various grades of General are at the top of the rank structure; but some countries have even higher ranks such as Field Marshal or Marshal. "General Officer", often referred to less formally and imprecisely as "General", refers to a military officer who holds any rank grade of General. The exact rank of a general may be determined by combining a prefix (e.g. Major General) or suffix (e.g. General of the Army). A General, without prefix or suffix (and sometimes referred to informally as a "full general"), is usually the most senior general officer rank, above Lieutenant General. In some armies, however, the rank of Captain General, General of the Army, Army General or Colonel General occupied or occupies this position. These ranks may be considered to be equivalent to a full General or to a Field Marshal, depending on the army in question. While historically an army rank, General is also used in most air forces, although those based on the British Royal Air Force use Air Marshal instead, with Air Officer being the generic title. In most navies of the world, the equivalent rank is Admiral and the generic term is Flag Officer; however a noteworthy historical exception was the Cromwellian naval rank General at sea. The rank of General began appearing around the time of the organization of professional armies in the 17th century. At first, it was added as an adjective to existing names of ranks, yielding Colonel General, Captain General, Lieutenant General and Sergeant Major General. These titles were used to distinguish the ruler's most important officers and usually involved a certain amount of negotiation over precedence. Lieutenant General is a military rank used in almost every country in the world. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages where the title of Lieutenant General was held by the second in command on the battlefield, normally subordinate to a Captain General. In most nations, a Lieutenant General ranks immediately below a General and above a Major General. The oddity in precedence, where a Lieutenant General outranks a Major General whereas a Major would normally outrank a Lieutenant, is caused by the rank of Major General previously having been known as Sergeant Major General, which was in turn subordinate to Lieutenant General. Major General or Major-General is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of Sergeant Major General. A major general is a high-ranking officer normally subordinate to a Lieutenant General and senior to a Brigadier General. In countries that do not maintain the rank of Brigadier General, including much of Eastern Europe, Major General normally serves as the lowest General Officer rank. Brigadier General (sometimes known as a one-star general from the United States insignia) is the lowest rank of general officer in some countries, usually ranking just above Colonel and just below Major General. Colonel is a military rank of a commissioned officer, with the corresponding ranks existing in nearly every country in the world. The rank of Colonel is one of the oldest in existence, dating as far back to the time of the Roman Empire. In the modern age, a Colonel is usually a military title rated as the highest field rank below the general grades. Lieutenant Colonel (Lieutenant-Colonel in British English) is a rank of commissioned officer in the armies and marine corps (and some air forces) of the world, typically ranking above a Major and below a Colonel. The rank of Lieutenant Colonel is often verbally shortened to simply "Colonel". Major is a military rank denoting an officer of mid-level command status. It is usually immediately superior to the rank of Captain and immediately subordinate to the rank of Lieutenant Colonel. In most comparative military scales a Major is ranked as a "Level 4" (O-4) officer although some systems (among them the NATO rank codes) list a Major as a Level 3. The naval equivalent to a Major is, in most nations, the rank of Lieutenant Commander. Captain is both a nautical term and a rank in various uniformed organizations. The word came to English via French from the Latin capitaneus ("chief") which is itself derived from the Latin word for "head" (caput). The term has different meanings both at sea and in the military. Confusion between the three types of captain (nautical, naval and army) often exists in literature, drama and real life. The customs indicated are necessary to avoid confusion at sea when the question of "Who is in charge of the ship?" may be a matter of life and death. The rank of Lieutenant has different meanings in different military formations (see comparative military ranks), but in all cases it is common for it to be divided. In the United States Army, Air Force and Marine Corps, First Lieutenant is the second-lowest ranking commissioned officer. It is one step above the rank of Second Lieutenant, usually promoted after 18 to 24 months service. A First Lieutenant usually leads more specialized platoons or may be the Executive Officer of a company-sized unit (110 to 140 personnel). In the United States Navy, First Lieutenant is a position title and is held by the officer in command of the Deck department. On smaller ships, a First Lieutenant holds the rank of Lieutenant Junior Grade. On larger vessels, the position is held by a Lieutenant or, in the case of extremely large warships such as aircraft carriers, a Lieutenant Commander or even full Commander. However, on US submarines, where the deck deparment may only have a few junior sailors, the First Lieutenant may be a senior enlisted member, such as a first class petty officer or chief petty officer. In Germany the rank of First Lieutenant is known as Oberleutnant, while in Poland as porucznik. Second Lieutenant is the lowest commissioned rank in many armed forces. In the United States, Second Lieutenant is typically the entry-level rank for most Commissioned Officers. A Second Lieutenant typically leads a platoon-size element (16 to 44 soldiers). In the United States Army, the rank bore no insignia until December of 1917, when a gold bar was introduced to contrast with the silver bar of a First Lieutenant. The rank is also used in the United States Air Force and the United States Marine Corps. As a result of the gold color of the bars, second lieutenants are often referred to colloquially as "Butterbars." The corresponding United States Coast Guard and United States Navy rank is Ensign. NON COMMISSIONED OFFICER (NCO) RANK STRUCTURE OF THE UNITED STATES AIR FORCE
The Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force (CMSAF) represents the highest enlisted level of leadership in the United States Air Force, and as such, provides direction for the enlisted corps and represents their interests, as appropriate, to the American public, and to those in all levels of government. He serves as the personal adviser to the Chief of Staff and the Secretary of the Air Force on all issues regarding the welfare, readiness, morale, and proper utilization and progress of the enlisted force. The Chevron for CMSAF was originally designed with chevrons that consisted of six lower and two upper ones. The current Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force is Gerald R. Murray. He was appointed to the position of Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force on July 1, 2002. Chief Murray is the 14th chief master sergeant appointed to the highest noncommissioned officer position. On November 1, 2004, the CMSAF insignia was updated to include the Great Seal of the United States of America and two stars in the upper field. The laurel wreath around the star in the lower field remained unchanged to retain the legacy of the Chief Master Sergeants of the Air Force. All Chief Master Sergeants, including the CMSAF, may also be referred to by the term "Chief." Chief Master Sergeant is the ninth, and highest, enlisted rank in the U.S. Air Force, just above Senior Master Sergeant, and is a non-commissioned officer. Chief Master Sergeants are addressed as "Chief." Attaining the rank of Chief Master Sergeant is the pinnacle of an enlisted Air Force member's career. Some Chiefs manage the efforts of all enlisted within their unit or major subsection thereof, while others run major staff functions at higher headquarters level. All Chiefs are expected to serve as mentors for junior and mid-grade commissioned officers as well as noncommissioned officers and to serve as advisors to commanders and senior officers. By Federal law, only one percent of the Air Force enlisted population may hold this rank. First Sergeant is the title given to holders of certain ranks and positions within the United States Armed Forces. While the specifics of the title may differ between the United States Army, Marine Corps and Air Force, all First Sergeants are non-commissioned officers and can be identified by the presence of a diamond, called a "French lozenge," on their rank insignia. Senior Master Sergeant is the eighth enlisted rank in the U.S. Air Force, just above Master Sergeant and below Chief Master Sergeant, and is a non-commissioned officer. Promotion to Senior Master Sergeant is the most difficult enlisted promotion to attain in the Air Force. It is the first enlisted grade to which results of a central promotion board are the primary factor in selection for promotion. Usually, less than ten percent of eligible Master Sergeants are selected for promotion to Senior Master Sergeant in most years. Selectees typically have vast technical and leadership experience gained from a broad variety of assignments at both line and staff functions throughout their careers. Additionally, the successful candidate will typically have at a minimum completed an associate's or bachelor's degree in their Air Force specialty as well as the Senior Noncommissioned Officer Correspondence Course and have had their latest performance report endorsed by a senior rater, usually a Colonel or Brigadier General. Senior Master Sergeants typically assume superintendent duties, overseeing enlisted members' efforts to accomplish a major segment of a unit's mission, in preparation for promotion to the rank of Chief Master Sergeant. They are expected to serve as mentors for noncommissioned and junior commissioned officers. Senior Master Sergeants in the First Sergeant special duty serve as First Sergeants of larger units than those employing a Master Sergeant as a First Sergeant. By Federal law, only two percent of the Air Force's total active duty enlisted strength may hold this rank.Senior Master Sergeants may be referred to by the nickname of "Senior". This usage is an informal one, however, and would not be used in an official or formal setting. Use of this nickname by Airmen of subordinate rank is at the rank holder's discretion. A Master Sergeant is the eighth enlisted rank in the United States Army, just above Sergeant First Class and below First Sergeant. It is abbreviated as "MSG." the eighth enlisted rank in the United States Marine Corps, just above Gunnery Sergeant, below Master Gunnery Sergeant, Sergeant Major, and Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps. It is equal in grade to First Sergeant. It is abbreviated as "MSgt." Master Sergeants in the U.S. Marine Corps provide technical leadership as occupational specialists at the E-8 level. General command leadership at this paygrade is provided by the separate rank of First Sergeant. the seventh enlisted rank in the United States Air Force, just above Technical Sergeant and below Senior Master Sergeant. It is abbreviated as "MSgt." Advancement to Master Sergeant is one of the most significant promotions within the enlisted Air Force. At the rank of Master Sergeant, the airman enters the senior noncommissioned tier and his or her duties begin to focus on leadership and management rather than technical performance. Per Air Force Instruction 36-2118, MSgts typically serve as flight chiefs (analogous to platoon sergeants in the US Army) and section chiefs (leaders of duty sections within a squadron). In the Marine Corps, Master Sergeants may be referred to by the nickname of "Top". This usage is an informal one, however, and would not be used in an official or formal setting. Use of this nickname by Marines of subordinate rank is at the rank holder's discretion. All Master Sergeants are non-commissioned officers. Technical Sergeant is the sixth enlisted rank in the U.S. Air Force, just above Staff Sergeant and below Master Sergeant. A technical sergeant is a non-commissioned officer and abbreviated as TSgt. Within the enlisted Air Force, promotion to TSgt has historically been the second most difficult rank to achieve (only the rank of Senior Master Sergeant, capped by Federal law, has lower promotion rates) and is the most difficult promotion most career Air Force members achieve. To be considered for promotion a Staff Sergeant must have 6 years time in service and 2 years as a Staff Sergeant. Technical Sergeants provide technical mentorship to junior enlisted members in preparation for entry into the senior noncommissioned tier and promotion to the rank of Master Sergeant. Technical Sergeant was also a rank in the United States Army until after World War II, when it was replaced by Sergeant First Class. Staff Sergeant is a rank of non-commissioned officer used in several countries. Senior Airman (SrA) is the fourth enlisted rank in the United States Air Force, just above Airman First Class and below Staff Sergeant. It has a US military pay grade of E-4. The Air Force promotes an Airman to Senior Airman upon a commander's recommendation after 36 months time in service and 20 months time in the grade of Airman First Class (A1C), or 28 months time in A1C, whichever comes first. Outstanding Airmen First Class, limited to no more than 15 per cent of the total, may be promoted to Senior Airmen six months early, a competitive process called Below-the-Zone (BTZ) which normally involves going before a competitive board. Senior Airmen are expected to be technically proficient and begin to develop leadership skills, and may be expected to supervise a younger airman. Senior Airmen are expected to attend the Airman Leadership School, which is part of the Air Force's Professional Military Education, before being promoted to Staff Sergeant. Formerly, this grade had two separate titles: Sergeant, which was considered to be a non-commissioned officer rank, and Senior Airman, which was the equivalent of Specialist in the United States Army. Senior Airmen were promoted to Sergeant after 12 months' time in grade and completion of the now-defunct Noncommissioned Officer Preparatory Course. The last Air Force promotions to Sergeant were effective May 1, 1991. Sergeants wore the same chevrons as present-day Senior Airmen. Senior Airmen wore similar chevrons, but lacking the central star. As with any change in policy, many airmen supported this change, while others protested. The grades of Senior Airman and Sergeant held the same pay grade, but Sergeants were expected to supervise other airmen as part of their duties as NCOs. Those against the change protested that the rank of Sergeant prepared airmen for transition to Staff Sergeant, and that new Staff Sergeants would therefore be less well-trained for their new position. Supporters argued that proper leadership training eliminated the need for a separate rank within the pay grade, and that the two ranks created disparity between individuals earning the same pay and benefits but with different workloads. Airman First Class (A1C) is the third enlisted rank in the United States Air Force, just above Airman and below Senior Airman. It is a member of the Airmen Tier of the Air Force Rank Structure, with the NCO and Senior NCO tiers being above it. Promotion to A1C occurs upon 10 months time in the grade of Airman, or earlier for Airmen with specific certain specialties, previous Junior Reserve Officer Training Corps (JROTC) experience, the Gen. Billy Mitchell Award in Civil Air Patrol, education levels or enlistment contract lengths. An A1C is considered to be fully adjusted to military life and his or her duties focus on honing job skills. Airman is a term used to refer to any enlisted personnel in the United States Air Force or Other Ranks in the Royal Air Force (in which airwoman is also seen). It is also a specific United States Air Force rank and United States Navy rate. More informally, it can refer to any member of an air force or to any pilot, military or civilian. In the United States Air Force, Airman (Amn) is the second lowest enlisted rank, just above Airman Basic and below Airman First Class. An Airman Basic is typically promoted to Airman after six months. An Airman's duties include adjusting to military life and becoming proficient in their Air Force specialty. In Federal Aviation Administration parlance, an airman is anyone in control of an aircraft. Airman Basic (AB) is the lowest enlisted rank in the United States Air Force, just below Airman. It is categorized as E-1 on the U.S. military pay scale. An Airman Basic's duties revolve around adjusting to military life. They are promoted to Airman upon their commander's recommendation after six months' time in grade. Airmen basic do not bear any uniform rank insignia, which would normally be worn on the sleeves. |
© AviationExplorer.com - The Website For Aviation Enthusiasts |